GitHub Actions is a powerful tool that allows developers to automate tasks and workflows within their GitHub repositories. One common use case is automating version tagging and release creation for software projects. In this tutorial, we will explore how to configure GitHub Actions to automatically create version tags and releases for a GitHub repository.
In this post, we are going to use GitVersion, which is a tool that generates a Semantic Version number based on your Git history. The version number generated from GitVersion can then be used for various different purposes, such as:
- Stamping a version number on artifacts (packages) produced during build.
- Exposing the version number to the build server to version the build itself.
- Patching
AssemblyInfo.cs(and similar) files with the version number during the build, so the version number is embedded within the compiled binaries themselves.
Requirements
- Github account
- Git cli tool
Configure GitHub Actions
To configure automatic version tagging and release creation, you will need to follow these steps:
- Step 1: Create a fork repository of this repo github-actions-demo in Github:
# You can fork this demo repository
# git clone fork
git clone https://github.com/cgn170/github-actions-gitversion-release.git
# Change to github-actions-gitversion-release directory
cd github-actions-gitversion-release
# Check the content of tag-release-version.yml file
cat .github/workflows/tag-release-version.yml- Step 2: Configure the workflow
Github uses a special directory called .github/workflows as the location for the configuration of the workflow in the repository.
Let’s take a look to the tag-release-version workflow in tag-release-version.yml file:
name: tag-release-version
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
create-tag-version:
name: Create Tag Version
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
outputs:
branchName: ${{ steps.gitversion.outputs.branchName }}
steps:
- name: Install GitVersion
uses: gittools/actions/gitversion/setup@v0.9.7
with:
versionSpec: '5.x'
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Determine Version
id: gitversion
uses: gittools/actions/gitversion/execute@v0.9.7
with:
useConfigFile: true
configFilePath: GitVersion.yml
- name: Display GitVersion outputs
run: |
echo "SemVer: ${{ steps.gitversion.outputs.semVer }}"
- name: Create tag
uses: actions/github-script@v3
with:
script: |
github.git.createRef({
owner: context.repo.owner,
repo: context.repo.repo,
ref: "refs/tags/v${{ steps.gitversion.outputs.semVer }}",
sha: context.sha
})
- uses: "marvinpinto/action-automatic-releases@latest"
with:
repo_token: "${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}"
prerelease: false
automatic_release_tag: v${{ steps.gitversion.outputs.semVer }}
This workflow will be triggered when a commit is pushed in the main branch with the following actions:
- Print the branch name
- Install GitVersion tool
- Clone the repo
- Build the version number based on GitVersion.yml file
- Create a tag in the repo with the version number
- Create an automatic release
Now, let’s take a look to the GitVersion.yml file:
mode: Mainline
tag-prefix: '[vV]'
commit-message-incrementing: MergeMessageOnly
branches:
hotfix:
regex: hotfix?[/-]
source-branches: ['main']
feature:
increment: Minor
regex: feature?[/-]
main:
is-mainline: true
increment: Patch
regex: main$
This GitVersion configuration is a simplified version of SemVer just to illustrate this demo.
- Step 3: Create a simple feature branch and merge it to the main branch
# Create feature/test2 branch
git checkout -b feature/test2
# Create a test file
echo "Hello world" > test2.txt
# Add the changes to the banch
git add --all .
git commit -m "added test2.txt file to branch"
# Push changes
git push --set-upstream origin feature/test2Create a pull request after pushing the changes in the feature branch and approve the merge pull request:
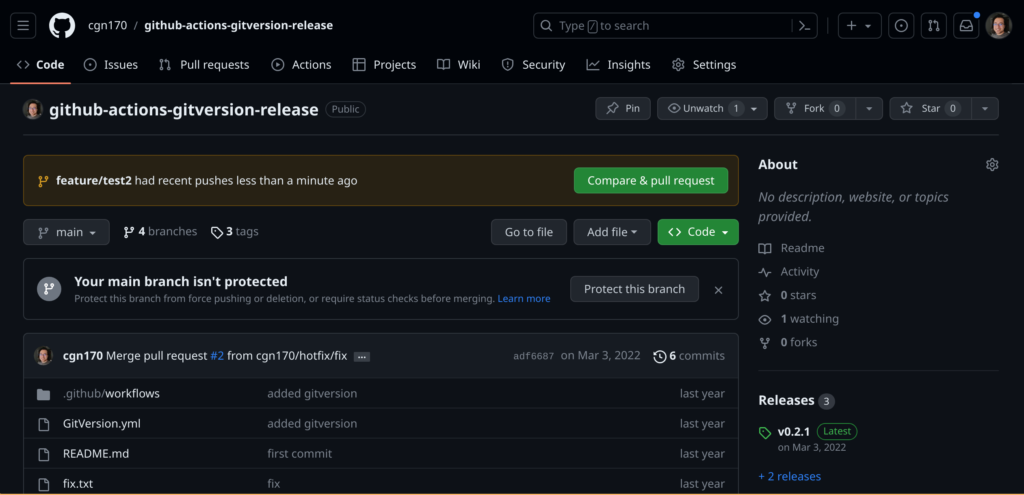
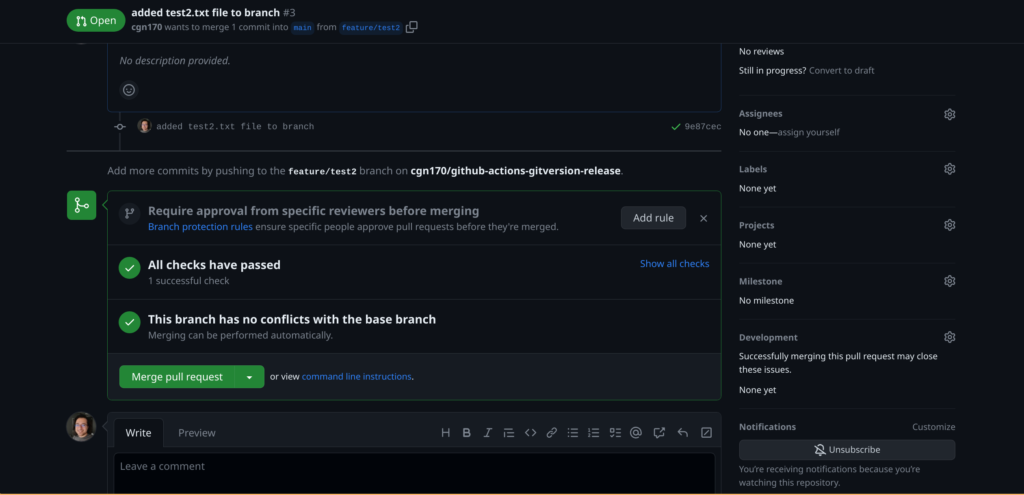
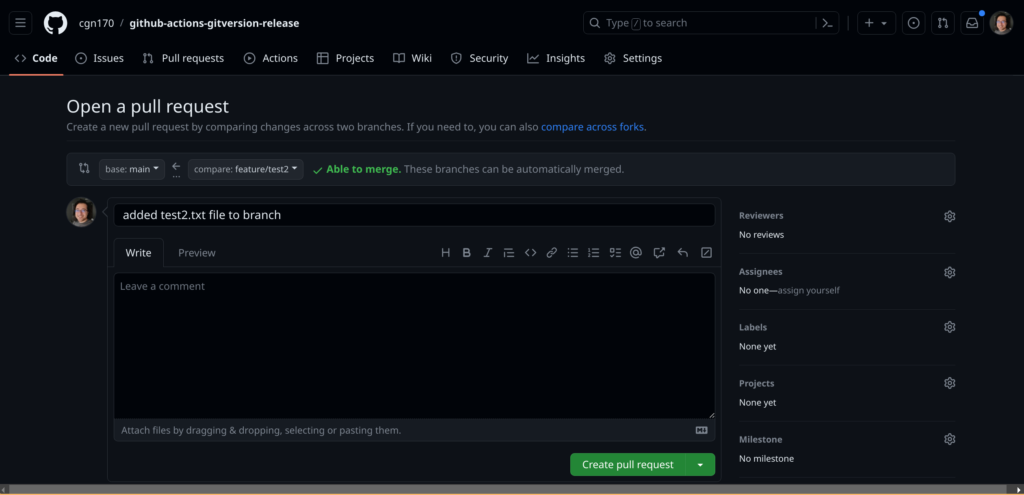
You can watch the progress of the Github actions workflow in the Actions Menu:
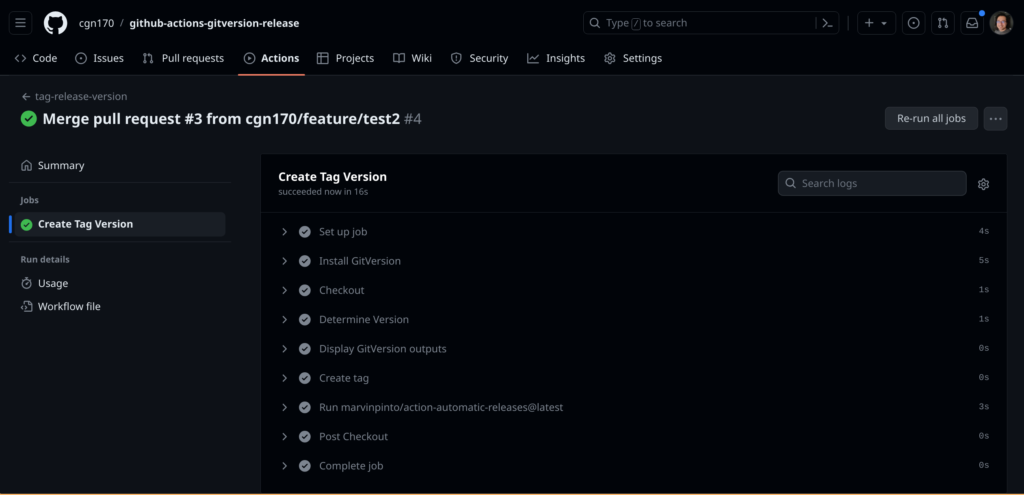
Once the workflow finishes check the new version number tag in the repo and the new release: