In this post I’m going to show you how to configure harbor registry inside minikube for local development in Kubernetes.
What is Harbor?
Harbor is an open source registry that secures artifacts with policies and role-based access control, ensures images are scanned and free from vulnerabilities, and signs images as trusted. Harbor, a CNCF Graduated project, delivers compliance, performance, and interoperability to help you consistently and securely manage artifacts across cloud native compute platforms like Kubernetes and Docker.
Before we start you’ll need the following requirements:
First, create the devops namespace and add Harbor helm repository:
# Create devops namespace
kubectl create namespace devops
# Add harbor helm repository
helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io
Install harbor helm package:
helm install registry harbor/harbor \
--namespace devops \
--set expose.type="clusterIP" \
--set expose.tls.enabled="false" \
--set registry.relativeurls="true" \
--set expose.clusterIP.name="harbor" \
--set expose.clusterIP.ports.httpPort="8080" \
--set externalURL="http://harbor.devops.svc:8080" \
--set harborAdminPassword="admin" \
--set registry.credentials.username="admin" \
--set registry.credentials.password="admin"Since we defined harbor.devops.svc as external url, we need to add it in the /etc/hosts file so our host can resolve the internally Harbor url.
sudo echo "127.0.0.1 harbor.devops.svc" >> /etc/hostsPort-forward harbor service to 8080 port.
kubectl port-forward -n devops service/harbor 8080:8080Now we have access to the harbor dashboard: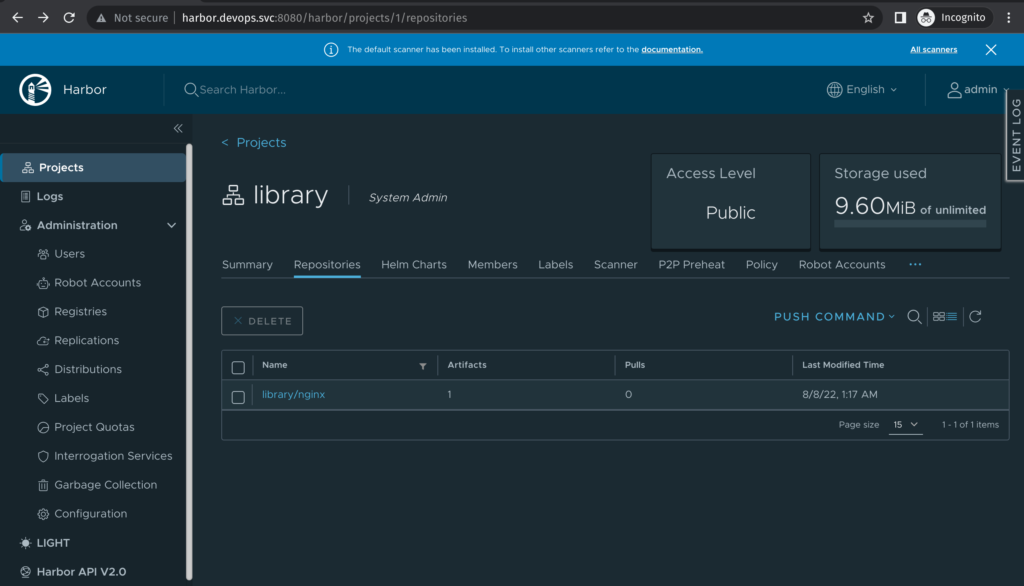
We can now login in the registry using docker:
docker login http://harbor.devops.svc:8080Let’s try to push a container image:
# Create a simple dockerfile
echo "FROM nginx" > Dockerfile
docker build . -t harbor.devops.svc:8080/library/nginx:latest
docker push harbor.devops.svc:8080/library/nginx:latest
# Run docker image locally
docker run --rm -p 8081:80 harbor.devops.svc:8080/library/nginx
# Check nginx docker
curl localhost:8081Harbor Inside K8s
To use harbor registry inside minikube you must add the address of the Harbor service to /etc/hosts file, the reason is that minikube can’t resolve the internal address of the Harbor service so we need to add it manually.
ssh -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null \
-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no \
-i $(minikube ssh-key) \
docker@$(minikube ip) \
"sudo /bin/sh -c 'echo $(kubectl -n devops get svc | \
grep -v '-' | \
awk '{print $3 " harbor.devops.svc"}') \
>> /etc/hosts'"Create a docker secret with the credentials, this is required by the pod to have access to the registry.
kubectl create secret docker-registry harbor \
--docker-server="harbor.devops.svc:8080" \
--docker-username="admin" \
--docker-password="admin"Finally create a pod and service with the image in the registry:
cat << EOF > pod.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: harbor.devops.svc:8080/library/nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http-web-svc
imagePullSecrets:
- name: harbor
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: nginx
ports:
- name: nginx
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: http-web-svc
EOF
# Deploy pod and svc in k8s
kubectl apply -f pod.ymlOnce is deployed, create a port-forward to have access to the pod:
# Port-forward nginx-service to port 8082
kubectl port-forward service/nginx-service 8082:80
# Check nginx service
curl localhost:8082We can check that the container image was successfully deployed.
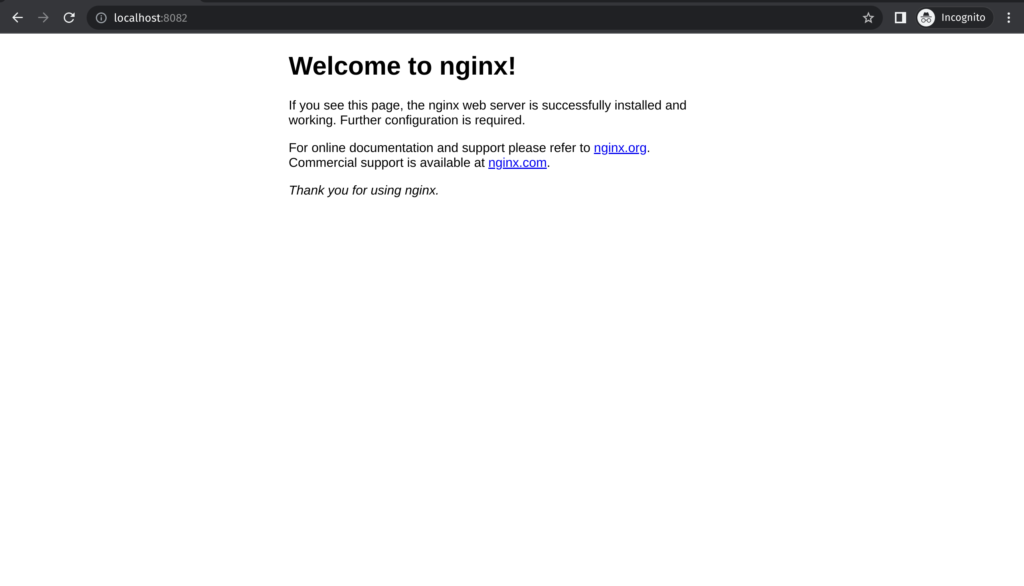
You can delete the deployment in minikube with the following commands:
# Uninstall harbor stack
helm uninstall registry -n devops
# Delete devops namespace
kubectl delete namespace devops
