What is Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC)?
Azure RBAC is an authorization system built on Azure Resource Manager that provides fine-grained access management to Azure resources.
Here are some things you can do with Azure RBAC:
- Allow an application to access all resources in a resource group.
- Allow one user to manage VMs in a subscription or any other resource.
- Allow a database administrator (DBA) group to manage SQL databases in a subscription.
- Allow an user to manage all resources in a resource group, such as VMs, websites, and subnets.
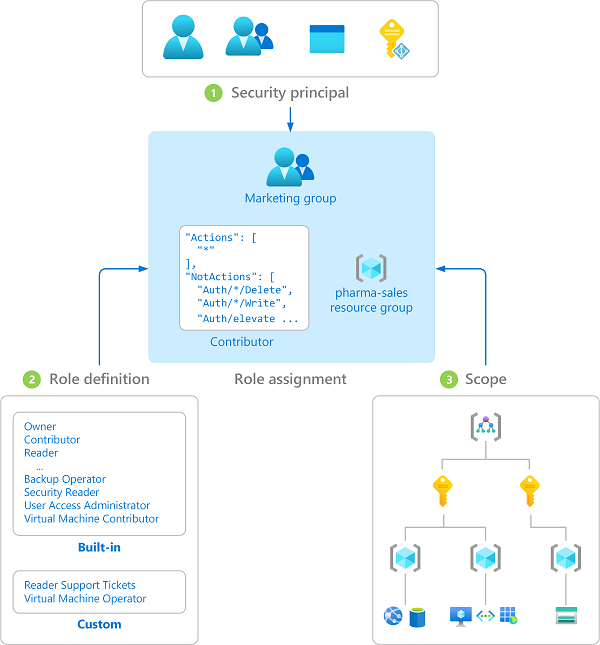
Create a role definition
A role definition is a set of permissions defined in a JSON file. Each permission set has a name, such as Actions or NotActions that describe the purpose of their permission. Some examples of permission sets include:
- Actions permissions identify what actions are allowed.
- NotActions permissions specify what actions aren’t allowed.
- DataActions permissions indicate how data can be changed or used.
- AssignableScopes permissions list the scopes where a role definition can be assigned.
The following diagram shows details for the Contributor role in Azure RBAC, which has three sets of permissions.
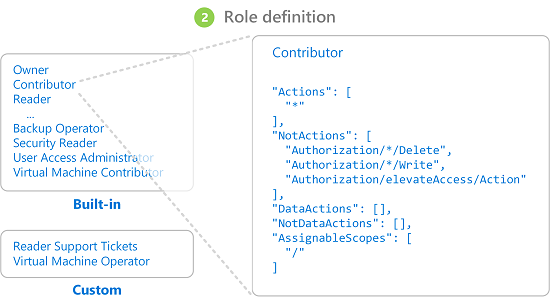
The Actions permissions shows Contributor role has all action privileges. The wildcard "*" means “all.” The NotActions permissions narrow the privileges provided by the Actions set, and deny three actions:
Authorization/*/Delete: Not authorized to delete or remove for “all.”Authorization/*/Write: Not authorized to write or change for “all.”Authorization/elevateAccess/Action: Not authorized to increase the level or scope of access privileges.
The Contributor role also has two DataActions permissions to specify how data can be affected:
"NotDataActions": []: No specific actions are listed. Therefore, all actions can affect the data."AssignableScopes": ["/"]: The role can be assigned for all scopes that affect data. The backslash{\}wildcard means “all.”
Role permissions
Use the Actions and NotActions permissions together to grant and deny the exact privileges for each role. The Actions permissions can provide the breadth of access and the NotActions permissions can narrow the access.

Role scopes
After you define the role permissions, you use the AssignableScopes permissions to specify how the role can be assigned. Let’s look at a few examples.
- Scope a role as available for assignment in two subscriptions:
"/subscriptions/c276fc76-9cd4-44c9-99a7-4fd71546436e", "/subscriptions/e91d47c4-76f3-4271-a796-21b4ecfe3624" - Scope a role as available for assignment only in the Network resource group:
"/subscriptions/c276fc76-9cd4-44c9-99a7-4fd71546436e/resourceGroups/Network" - Scope a role as available for assignment for all requestors:
"/"
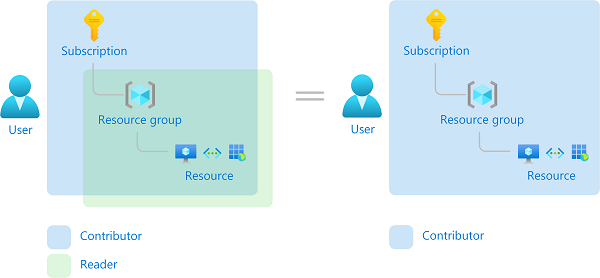
Things to consider when assigning scope levels for roles
The following diagram shows an example of how scopes can be applied for a role to grant varying levels of access for different users. Think about how we can implement scopes roles to create meaningful assignments for your organization.
Review fundamental Azure RBAC roles
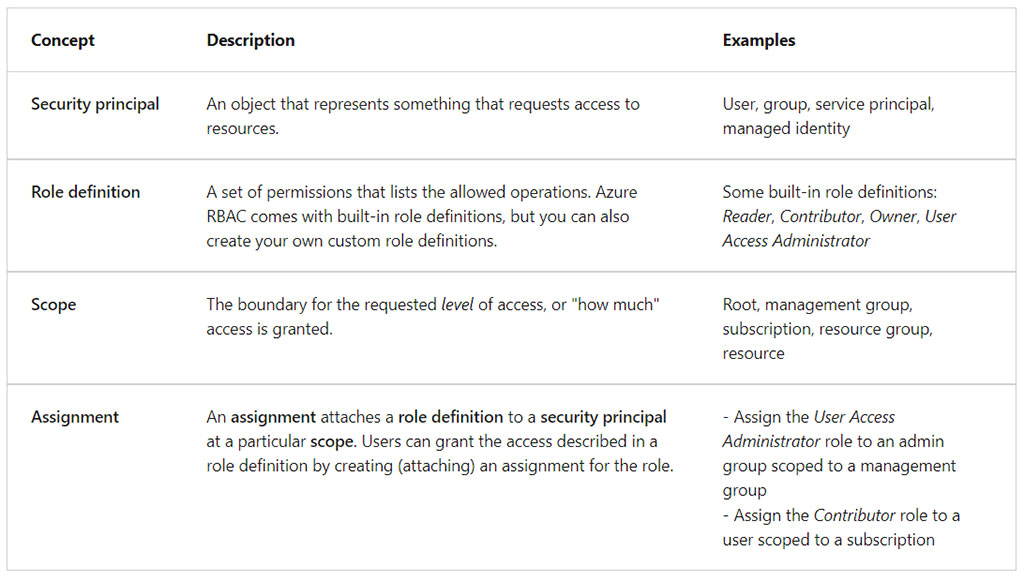
Azure RBAC provides over 100 pre-defined role definitions. Roles can grant access to data within an object. If an user has read data access to a storage account, then they can read the blobs or messages in the storage account.
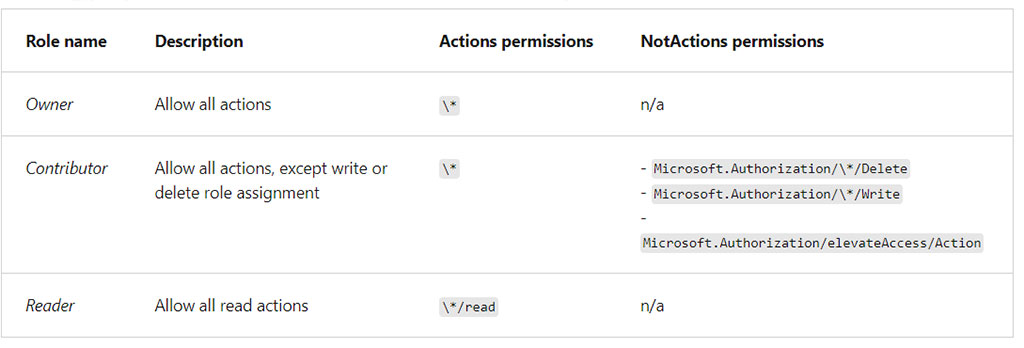
The following table describes four built-in Azure RBAC role definitions that are considered fundamental.
Role definition and structure
A custom role definition breaks down into a collection of different permissions. Each definition details the operations that are allowed, such as read, write, and delete.
The definition is formed using these structures:
{
"Name": "",
"IsCustom": true,
"Description": "",
"Actions": [],
"NotActions": [],
"DataActions": [],
"NotDataActions": [],
"AssignableScopes": [
"/subscriptions/{subscriptionId1}"
]
}The following example shows the role definition for the Contributor role:
{
"Name": "Contributor",
"Id": "b24988ac-6180-42a0-ab88-20f7382dd24c",
"IsCustom": false,
"Description": "Lets you manage everything except access to resources.",
"Actions": [
"*"
],
"NotActions": [
"Microsoft.Authorization/*/Delete",
"Microsoft.Authorization/*/Write",
"Microsoft.Authorization/elevateAccess/Action",
"Microsoft.Blueprint/blueprintAssignments/write",
"Microsoft.Blueprint/blueprintAssignments/delete"
],
"DataActions": [],
"NotDataActions": [],
"AssignableScopes": [
"/"
]
}Any role definition is declared using the following format:
{Company}.{ProviderName}/{resourceType}/{action}The action portion is typically one of the following actions:
Quick start management RBAC using Azure CLI
Below we have a summary with the most used commands to manage Azure RBAC services.
To grant access, you assign roles to users, groups, service principals, or managed identities at a particular scope.
az ad user show --id "{principalName}" --query "id" --output tsvAzure role assignment condition is an additional check that you can optionally add to your role assignment to provide more fine-grained access control.
az role assignment create --role "Storage Blob Data Reader" --scope /subscriptions/mySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/myResourceGroupName --scope /subscriptions/mySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/myResourceGroupName --assignee "user1@contoso.com" --resource-group {resourceGroup} \
--description "Read access if container name equals blobs-example-container" \
--condition "((!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'})) OR (@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers:name] StringEquals 'blobs-example-container'))" \
--condition-version "2.0"If an Azure built-in roles doesn’t meet the specific needs of your organization, you can create your own custom roles.
az role definition create --role-definition {roleDefinition}
az role definition update --role-definition {roleDefinition}To determine what resources users, groups, service principals, or managed identities have access to, you list their role assignment.
az role assignment list --subscription {subscriptionNameOrId}In Azure CLI, you can remove a role assignment by using az role assignment delete.
az role assignment delete --assignee "22222222-2222-2222-2222-222222222222" \
--role "Reader" \
--subscription "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"Contact us for more information or visit our blog.

